NESS automations from Live with Max4Live plugin
Windows & Mac
This tutorial show you step by step how to control the audio objects in NESS from Ableton Live.
To learn how to route audio from Live to NESS with Blackhole on a Mac, follow this tutorial: Routing audio from any DAW to NESS (Mac Only)
For a more complete tutorial on the use of automations in Ableton, please refer to the following tutorial: Working with Automation and Modulation
Installation of the Max4Live NESS plugin
The NESS_source_control plugin is a max for live plugin, allowing to create OSC automations from Ableton Live to control the positions and parameters of audio objects in NESS. We will use it to record the movements as automations in Live tracks and playback those movements in NESS.
The plugin can be downloaded on the APG website: Ableton Plugin | APG
Windows
- 1. Just unzip the whole content of the zip file in the following folder :
C:\Users\USERNAME\Documents\Ableton\User Library\Presets\Audio Effects\Max Audio Effect
Tip : the User Library folder of Ableton can be accessed by right-clicking the “User Library” icon in the Places section on the left of Ableton Window
- 2. Click on “show in explorer” to open the folder
Mac
- 1. Just unzip the whole content of the zip file in the following folder :
HD\Users\USERNAME\Music\Ableton\User Library\Presets\Audio Effects\Max Audio Effect
Tip : the User Library folder of Ableton can be accessed by right-clicking the “User Library” icon in the Places section on the left of Ableton Window
2. Click on “show in Finder” to open the folder
Presentation of the plugin
The plugin reuses the UI of the source position panel in NESS and of the movements’ management.
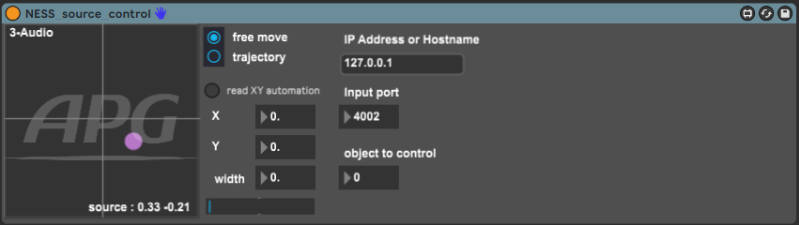
- X → X coordinate of the source (between -1 and 1, it is automatically rescaled in NESS)
X is available for automations - Y → Y coordinate of the source (between -1 and 1, it is automatically rescaled in NESS)
Y is available for automations - XY Pad → to visualize and control the source position
- Read XY automation → should be enabled to read recorded automations
- Width → perceived width of the source (between 0 and 1)
Width is available for automations - IP Address → IP Address of the computer on which NESS is running
- Input port → UDP port number to receive the source parameters values from NESS
- Object to control → ID of the source to control in NESS (between 1 and 16, 0 deactivates the remote control)
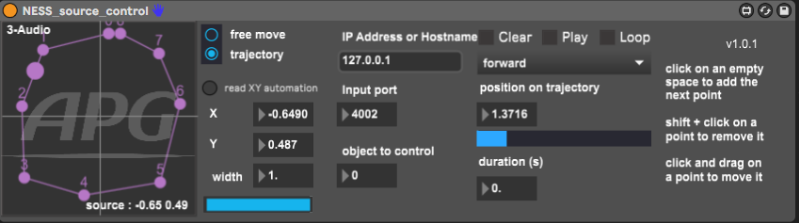
In free move mode, the trajectory controls are displayed:
- Clear → delete all trajectory points
- Play → triggers the movement
Play is available for automations - Loop → plays the movement in loop
- Direction → direction of the movement: forward, reverse or round trip
- Position on trajectory → sets the position of the source on the trajectory.
Example: if the index is set to 3.5 the source will be placed in between the points 3 and 4 of the trajectory - Position slider → sets the position of the source on the trajectory between 0 and 1(0 is the beginning of the trajectory, 1 is the last point)
Position slider is available for automations - Duration → total duration of the movement when triggered with the Play button
Configuring the plugin in Ableton Live
The NESS_source_control plugin can be loaded on Live tracks just by dragging and dropping it on the tracks to automate.
- 1. Open a new or existing project in Ableton Live
- 2. Activate the audio engine (it is required to enable the controls of the plugin)
- 3. In the left panel, go to Max for Live > Max Audio Effect
- 4. Select the plugin NESS_source_control and drop it on each track on which automations must be performed
- 5. Enter the IP of the computer on which NESS runs in the “IP Address or Hostname” field. This should only be done for one plugin. All other NESS plugins of the sessions will automatically take the same value.
If NESS is running on the same computer as Live, the IP address should be 127.0.0.1 - 6. Set the input port to the value of your choice. This value will be reused to configure the bidirectional control in NESS. This should only be done for one plugin. All other NESS plugins of the sessions will automatically take the same value
- 7. Set the ID of the object to control in NESS. This should be different for each instance of the plugin.
- 8. Save the session.
Configuring the OSC communication in NESS
The OSC communication must be configured in NESS in order to enable the remote control.
The communication is bidirectional, meaning that you can control the positions of NESS objects from Live with the plugin, but you can also control the parameters of the plugin from NESS. It is particularly useful if you use it in combination with the TouchOSC template, or if you want to record a live performance with pre-programmed movements of sources in NESS.
- 1. Open NESS
- 2. Open a new or an existing session in NESS
- 3. Go to the Settings page
- 4. In the OSC Settings section, configure one of the available device to send OSC to Live:
- a. Name the chosen device “Live”
- b. Enter its IP address, it should be the address of the computer on which Live is running
- c. Enter the port number, it should be the same as configured in the Live plugin.
- d. Enable the OSC send to this device
- e. Enable “Receiving OSC”
- f. Save the snapshot.
Note: the OSC device configuration is automatically replicated on all other snapshots
Using the Max4Live Plugin
Once Live and NESS configured, in Live, reopen the live project configured with the plugins.
At the loading of the project in Live, all audio objects in NESS should take the name and the color of the corresponding track in Live. All objects positions in NESS are set according to the XY Pad of each plugin in Live.
- At this point:
- If you move a source from the plugin, you should see the source moving in NESS.
- If you change the width of the source in the plugin, you should see the width parameter updated in NESS.
- If you change the name or the color of the track on which the plugin is loaded, the remote object in NESS should be renamed and its color updated.
- If you trigger a movement from the plugin, the controlled source must be moving in NESS
Switch to the Arrangement view of live in the upper right corner
Recording and playing back Automations in Live
Configuring the automations

Switch to the Arrangement view of live in the upper right corner

Enable the automation mode
On the track on which the automation must be recorded, for each parameter to automate:

1. Select NESS_source_control in the plugin selection menu

2. Select the parameter to automate in the parameter selection menu

3. Click on “+”,
The parameter is ready to be automated.
Try to configure the automations for X, Y and width parameters and move the source in the XY Pad of the plugin. The red dotted lines should move in the arrangement view.
Recording and playing back a movement
Once the X and Y parameters automations have been configured, you can record a movement simply by pressing the record button at the top of the window and moving the source in the XY pad. Make sure that the read XY automation button is deactivated. Automation curves should be drawn on the track.
- 1. Arm the automations with the button on the upper controls bar

- 2. Launch the recording
- 3. Move the source with the mouse in the XY pad
- 4. Stop the recording
- 5. Enable “read XY automation” next to the XY pad
- 6. Play back the automation, the movement must be reproduced in the XY pad
Controlling the parameters from NESS
The automations can be recorded as long as the x and y parameters change in real time. Thanks to the bidirectional OSC communication with NESS, the parameters can be controlled from NESS. Instead of moving the source in the XY Pad of the plugin, the source could be moved in NESS.
Using the trajectory editor of the plugin
The movement can also be created with the trajectory editor by automating only the position slider. These functions allow to finely rework the movement by manipulating the trajectory points instead of recording a freehand trajectory.
Troubleshooting
If your plugin looks like that, it means that Ableton Live did not find the trajectory tool.

- Go to the Max for Live section in the left panel
- In Max Audio Effect, right click on NESS_source_control
- Select “show in finder”.
- Download the trajectory library xydisplay
- Place it in the folder next to the file NESS_source_control.amxd. Replace the existing one if it already exists
- Close and relaunch Ableton Live
- Try to reload the plugin, it should be fixed !
